Male Hormones and Sleep: How Sleep Affects Testosterone Levels
June 24, 2025
Low testosterone: Effects on fertility and potential solutions
September 16, 2025Blood Testosterone and Physical Activity: How to Stay Healthy with Proper Exercise
Testosterone is the primary male hormone, responsible for sexual function, maintaining muscle mass, regulating metabolism, and supporting psychological well-being. As we age, blood testosterone levels gradually decline, which can lead to fatigue, decreased libido, increased body fat, and loss of strength. However, systematic physical activity has been proven to help support its natural production and contribute to maintaining higher levels.
In this article, we will analyze which types of exercise have the most beneficial effect on blood testosterone, how to incorporate them into your routine, and which mistakes to avoid in order to enjoy the benefits safely.
What affects blood testosterone levels
Testosterone is mainly produced in the testes and is regulated by the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland, two areas of the brain that control hormonal balance. Beyond age, several factors influence its levels:
Stress and elevated cortisol
Poor sleep
Poor diet and vitamin deficiencies (especially zinc and vitamin D)
Obesity
Sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise
Exercise is one of the most important ways to naturally increase blood testosterone and improve overall health.
How exercise affects testosterone
Physical activity acts through multiple mechanisms:
It increases muscle mass, which is associated with higher testosterone
It reduces visceral fat, which negatively affects hormones
It improves insulin sensitivity and metabolism
It helps regulate cortisol, the stress hormone
It increases blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues
Studies have shown that even moderate training can lead to improvements in blood testosterone levels, especially in men who previously had low physical activity.
Which types of exercise help the mostΠοιοι τύποι άσκησης βοηθούν περισσότερο
Not all forms of exercise have the same effect on hormones. The most beneficial are:
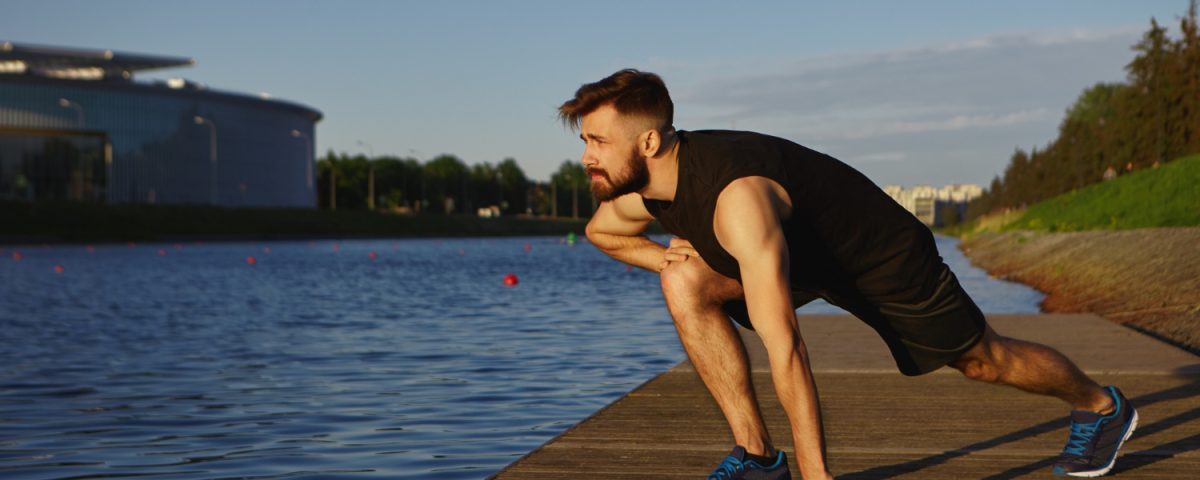
Resistance training (weightlifting): Lifting weights and strength exercises cause an increase in blood testosterone immediately after training and help maintain it long-term. Compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, and presses have the greatest impact.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT): Alternating short bursts of intense effort with recovery periods, HIIT activates metabolism and has been shown to boost testosterone more effectively than prolonged aerobic exercise.
Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise: Running, cycling, and swimming at moderate intensity are beneficial for cardiovascular health and indirectly support normal hormone levels.
How often you should exercise
For optimal results, it is recommended to:
Do 2–3 sessions of resistance training per week focusing on large muscle groups
Include 1–2 HIIT sessions lasting 20–30 minutes
Walk or do light aerobic activity on the remaining days
Consistency is key: it’s better to do a little exercise every week than to have long periods of inactivity followed by sudden intense efforts.
What to watch out for to avoid the opposite effect
Excessive training can lead to the opposite results. Very intense or prolonged exercise without adequate rest increases cortisol, which suppresses testosterone production.
Therefore:
Make sure you sleep at least 7–8 hours
Maintain a balanced schedule of training and recovery
Consume enough protein, quality carbohydrates, and healthy fats
Don’t skip post-exercise recovery
If you experience persistent fatigue or a sudden drop in performance, consider the possibility of overtraining and consult a specialist.
The role of diet and lifestyle
Exercise alone is not enough to maintain healthy blood testosterone levels. Diet, sleep, and stress management are equally important. To support training results, it is essential to get sufficient intake of key micronutrients such as zinc, magnesium, and B vitamins. These directly contribute to testosterone synthesis and endocrine regulation.
Adequate hydration, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a stable body weight are additional factors that can enhance the effects of physical activity. On the contrary, a diet poor in nutrients or high in processed foods and trans fats is linked to lower testosterone levels and difficulty maintaining muscle mass.
Sleep is another crucial pillar. During deep sleep, a significant amount of testosterone is secreted. Chronic sleep deprivation not only reduces its production but also increases cortisol, further burdening hormonal balance. If you struggle to get enough sleep, consider changes to your daily habits, such as avoiding screens before bedtime, limiting caffeine, and establishing a consistent relaxation routine.
When to check your blood testosterone levels
Exercise is a valuable ally, but if you experience symptoms such as:
Decreased libido
Decreased libido
Reduced muscle strength
Unexplained fat gain
Depressed mood
it is necessary to get your blood testosterone levels checked. A simple blood test can determine if your values are below normal and help design an appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
Blood testosterone significantly affects men’s health, strength, and quality of life. Regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and quality sleep are the strongest tools to naturally support its normal production. With consistency, adequate rest, and regular monitoring, you can maintain hormonal balance and feel strong and healthy at any age.